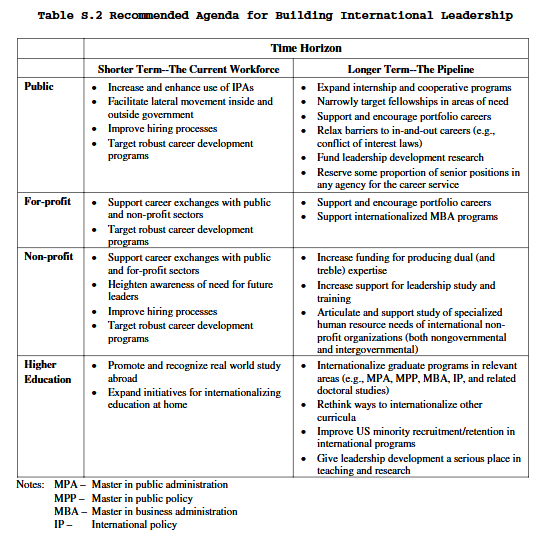
Two Key Competencies for Global Leadership
Featured Image Courtesy of Bikson et al., 2003, p. xxii, Table S.2
Cross-Cultural Competence (Bikson et al., 2003): the ability to interact with individuals from cultures other than one’s own effectively (as per their customs, values, and circumstances). It encompasses multicultural sensitivity, which is not acquired through study but through life experiences and living/working in another culture, and ideally, learning a second language. According to Gough (2022, p. 2, para. 1), diversity among multicultural teams contributes to increased creativity and serves as a “basis for synergy.”
Global Scope of Practice (Bikson et al., 2003): Leaders must see the big picture that situates their organization in an international context. This may involve considerations related to what it actually means to work in different locales and what it means to tackle international markets, politics, and cultural practices. In a global marketplace, adaptation and mastery of the learning curve are of utmost necessity to remain efficient and effective as leaders managing “task and relationship processes” (Gough, 2022, p. 3).
Preparation for Science, Technology & Education Growth 2023 - 2033 (Blatt, 2022)
Featured Image Courtesy of Poister et al. (2015, p. 7)
Figure 2 depicts NASA education programs at the bottom of their list of priorities. This serves as a public indication of an area needing further development. A Space Foundation-sponsored mentorship program for experienced space professionals to mentor students and the next generation of space leaders to advance STEM education and workforce development throughout the global space community is an area of expertise that many think is out of reach. Considering the DEI areas within the United States government have been closed and the responsibility redirected at companies to manage internally, a program could be created using a model of SMART goals, namely, Specific (mentor-mentee matching in STEM fields), Measurable (measuring participation or engagement), Achievable (making use of networking collaboration already present and/or create new y pairing off NPOs with NGOs), Relevant (connected to education and workforce development), and Time-bound (have a pilot within 12 months). This approach welcomes social reform to activate career paths in space and/or engineering and enhance diversity in the workforce. According to Torpey (2025), the Bureau of Labor Statistics identified in ‘chart 1’ that scientific, technology, and research industries are at the top with expected exponential growth up to 2033. Therefore, the mastery of education will be needed to fulfill the research aspect to continue innovative development.

Assessing Resource Development Trends for 2025
Featured Figure 1
Power Cells on the Moon to advance humanity despite depleting resources on Earth (Bausback, 2024, Image 1)
Implications on Resource Development Strategies (RDS):
The attention of the wider society, with a growing focus on global environmental sustainability, has shifted development strategies to how we can use fewer resources. For J2 Rescue & Rehab, Inc. (J2RRINC.org), this trend signals the need for sustainable acumen adoption for wildlife conservation, restoration, programs, and partnerships (McNay, 2020). J2RRINC.org can align its strategies and practices with eco-friendly doctrines and promote biodiversity conservation in compliance with UN SDGs (Kerr, 2025).
